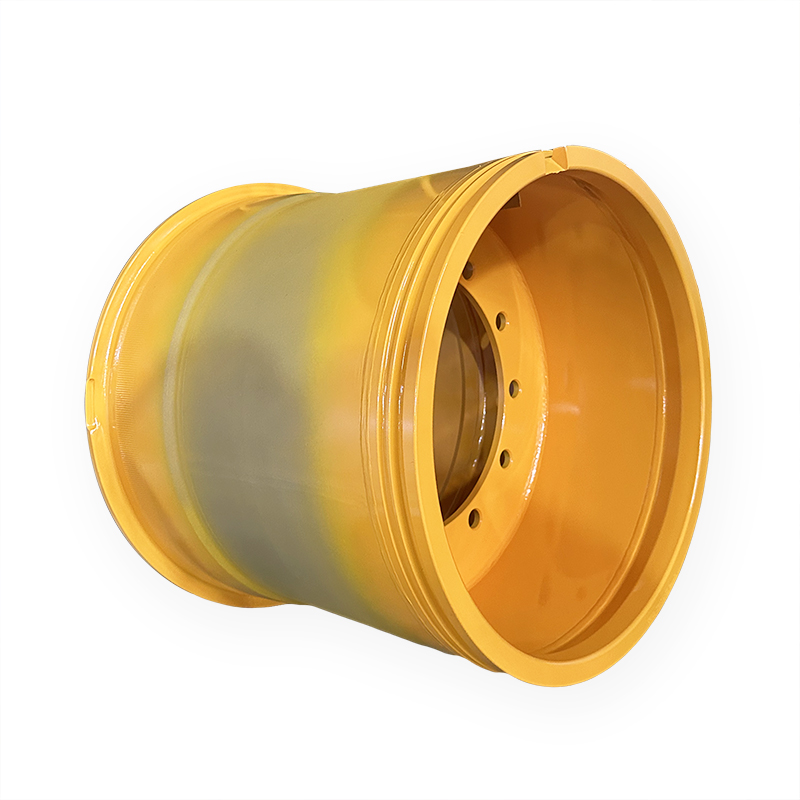
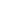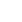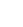19.50-25/2.5 rim for Construction equipment Wheel Loader LJUNGBY
Wheel Loader
Wheel loaders are made up of several key components that work together to perform various functions and tasks. While the specific design may vary by manufacturer and model, the following are common components found in most wheel loaders: 1. Frame: The frame is the main structural backbone of a wheel loader and provides support for all wheels. The loader provides support and stability to other components. It is usually made of high-strength steel and is designed to withstand heavy loads and harsh operating conditions. 2. Engine: The engine powers the wheel loader and provides the propulsion and hydraulic power required to operate the machine. Wheel loaders usually come with diesel engines, but some smaller models may run on gasoline or electric power. 3. Transmission: The transmission transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the operator to control the speed and direction of the wheel loader. It can be manual, automatic or hydrostatic, depending on the model and application. 4. Hydraulic System: The hydraulic system controls the movement of the loader arm, bucket, and other attachments. It consists of a hydraulic pump, cylinders, valves, hoses, and reservoirs that work together to provide fluid power for lifting, lowering, tilting, and other functions. 5. Loader Arm: The loader arm, also known as the lift arm or boom, is mounted on the front of the wheel loader and supports the bucket or attachment. They are hydraulically operated and can be raised, lowered and tilted to control the position of the bucket. 6. Bucket: A bucket is a front-mounted attachment used for scooping and moving materials such as soil, gravel, sand, rocks and debris. Buckets come in a variety of sizes and configurations, including general-purpose buckets, multi-purpose buckets and specialized attachments for specific tasks. 7. Tires: Wheel loaders are equipped with large, heavy-duty tires that provide traction and stability on a variety of terrains. Tires can be pneumatic (air-filled) or solid rubber, depending on the application and operating conditions. 8. Operator Cab: The operator cab is the enclosed compartment where the operator sits while operating the wheel loader. It is equipped with controls, instrumentation, seating and safety features to provide the operator with a comfortable and safe working environment. 9. Counterweight: Some wheel loaders are equipped with counterweights at the rear of the machine to offset the weight of the engine and other components at the front. This helps improve stability and balance during operation, especially when lifting heavy objects. 10. Cooling System: The cooling system helps regulate the temperature of the engine and hydraulic components by dissipating the heat generated during operation. It usually consists of a radiator, cooling fan and related components. These are some of the main components of a typical wheel loader. Depending on the model and application, there may be additional features, accessories or optional components customized to specific needs and preferences.
More Choices
Production Process
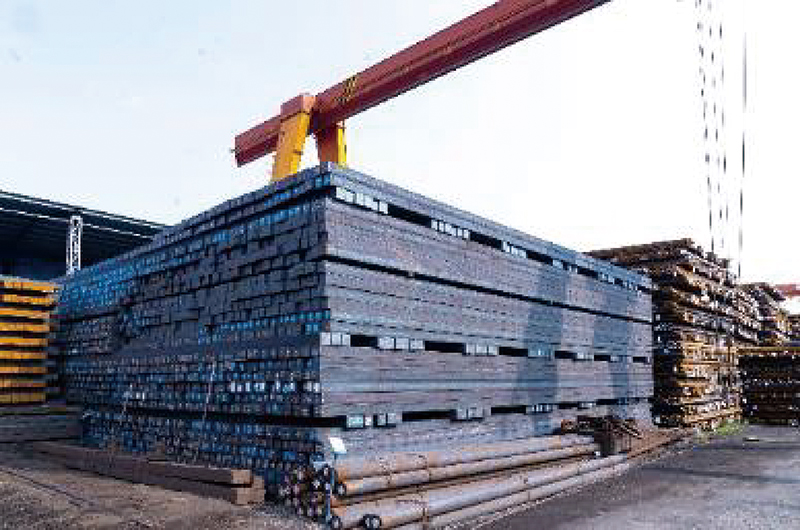

1. Billet

4. Finished Product Assembly
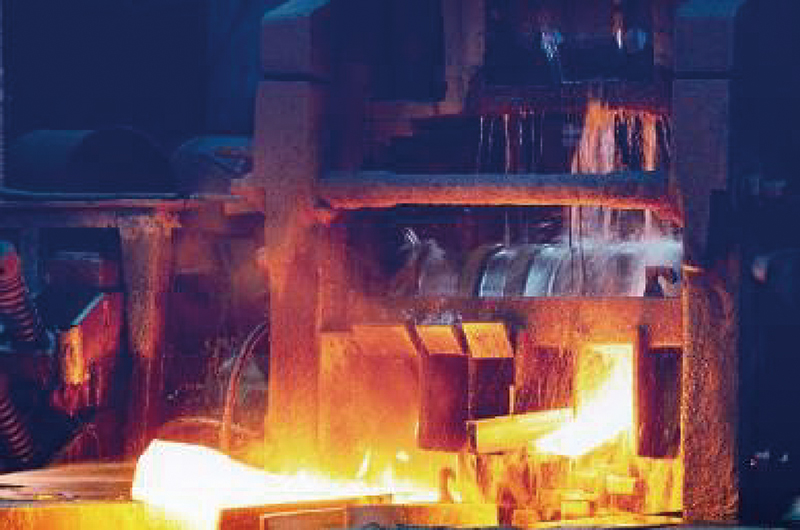

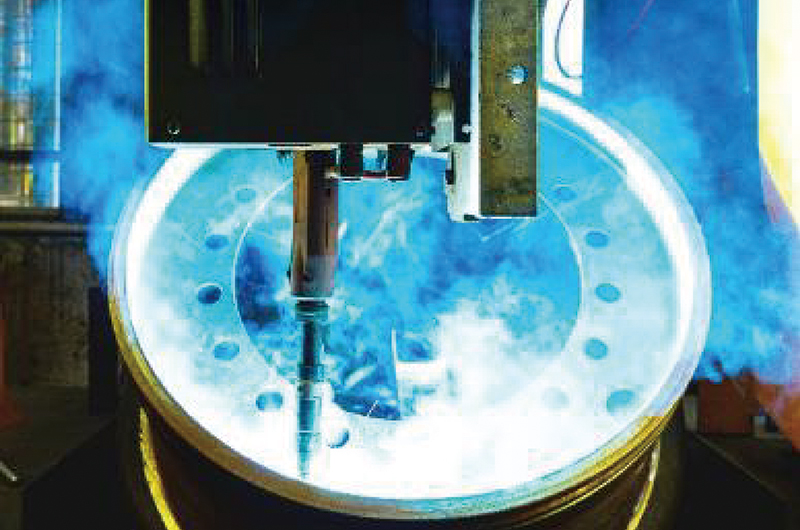
2. Hot Rolling
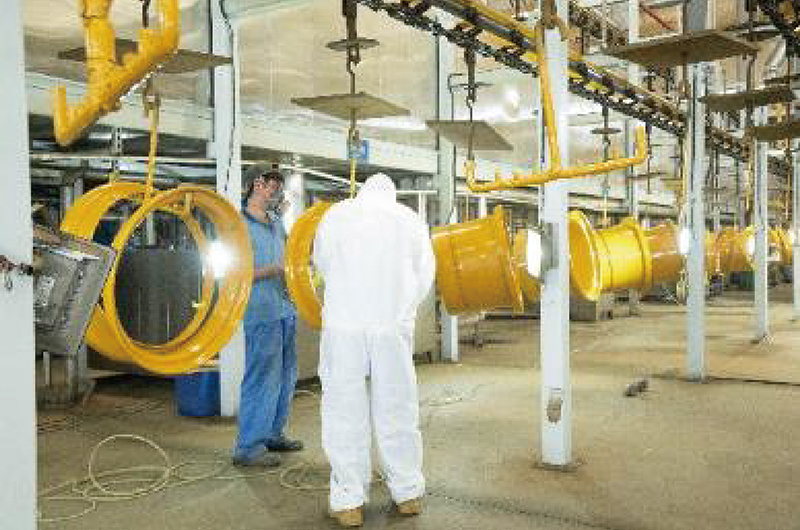

5. Painting
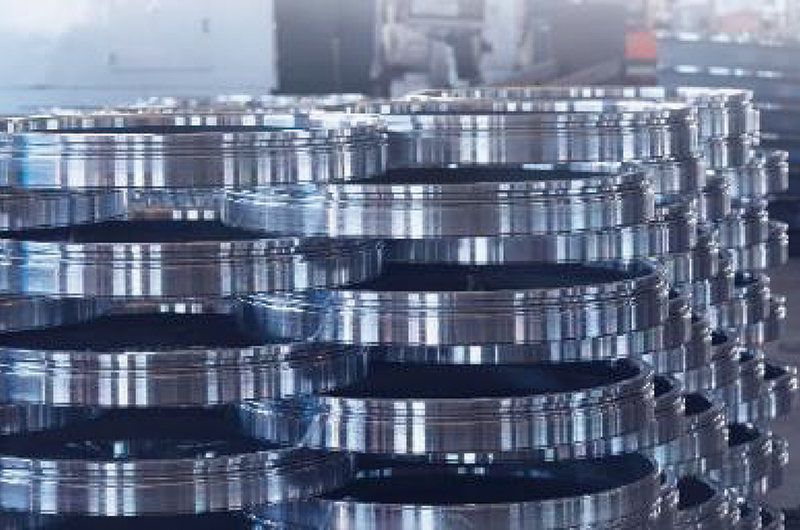

3. Accessories Production
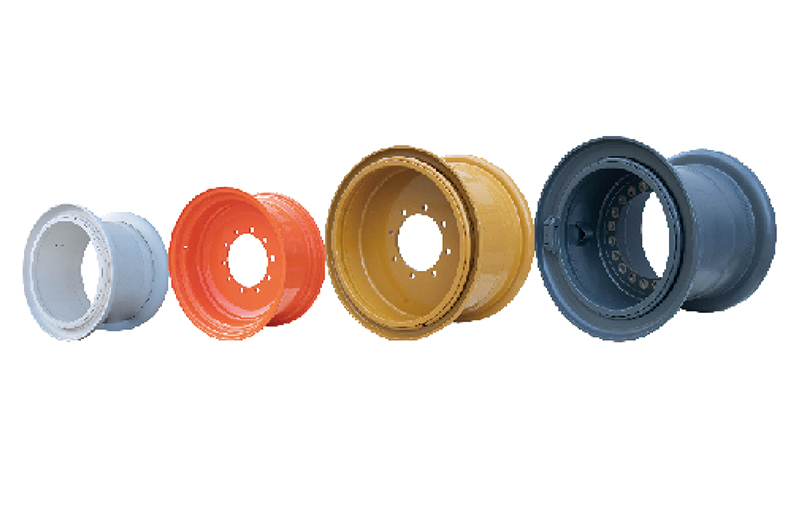

6. Finished Product
Product Inspection
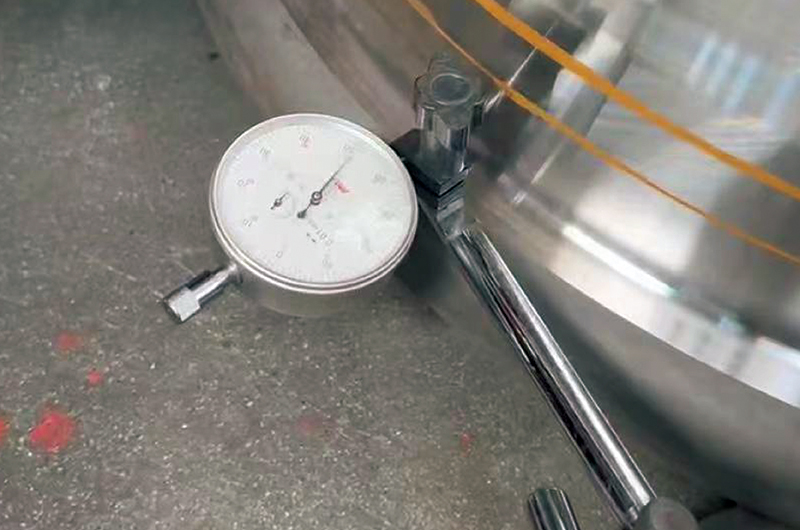

Dial indicator to detect product runout
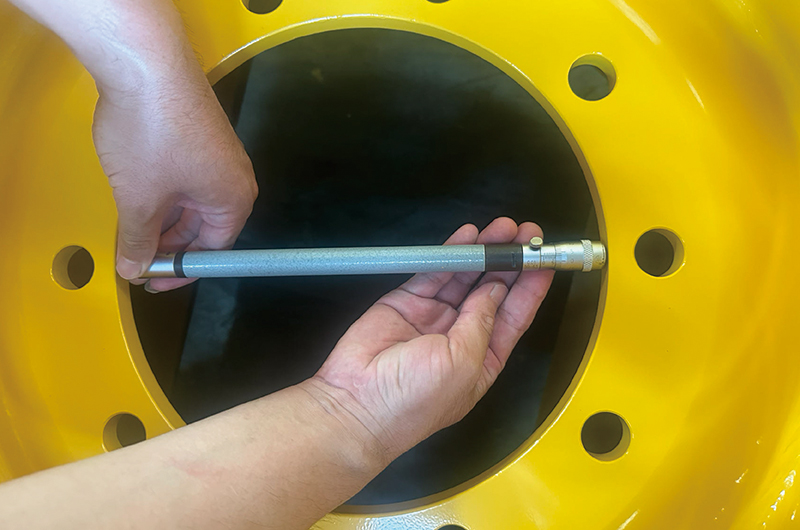

External micrometer to detect internal micrometer to detect the inner diameter of the center hole

Colorimeter to detect paint color difference
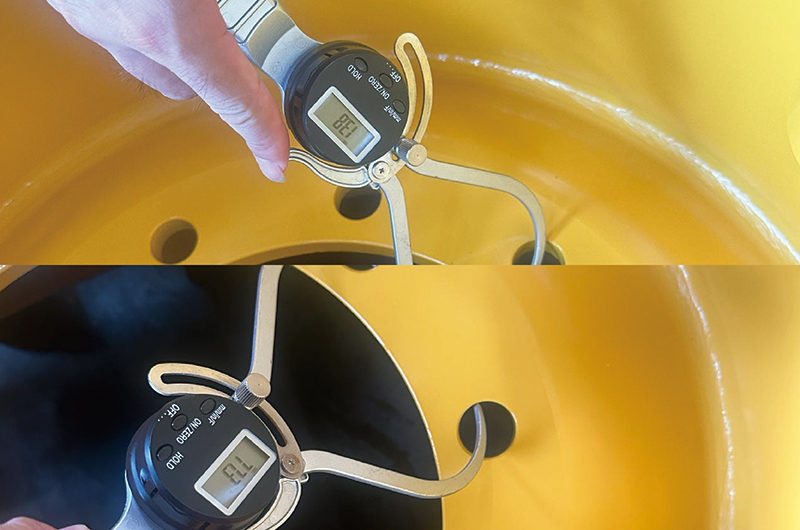

Outside diametermicromete to detect position
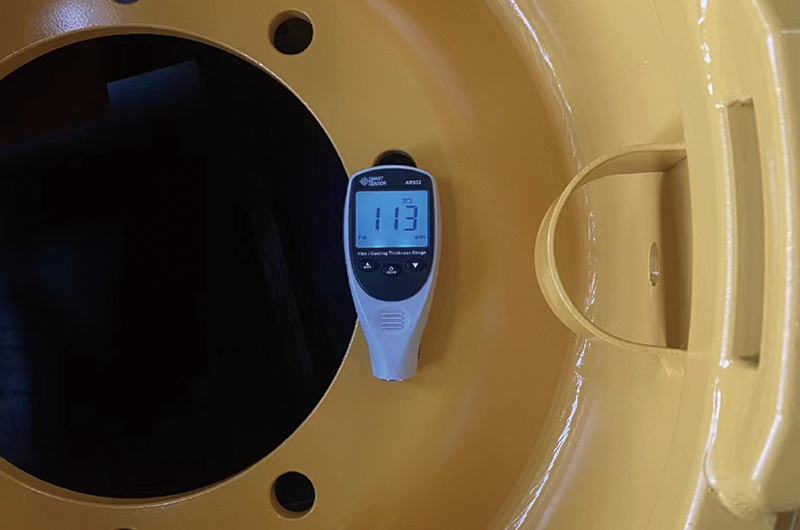

Paint film thickness meter to detect paint thickness
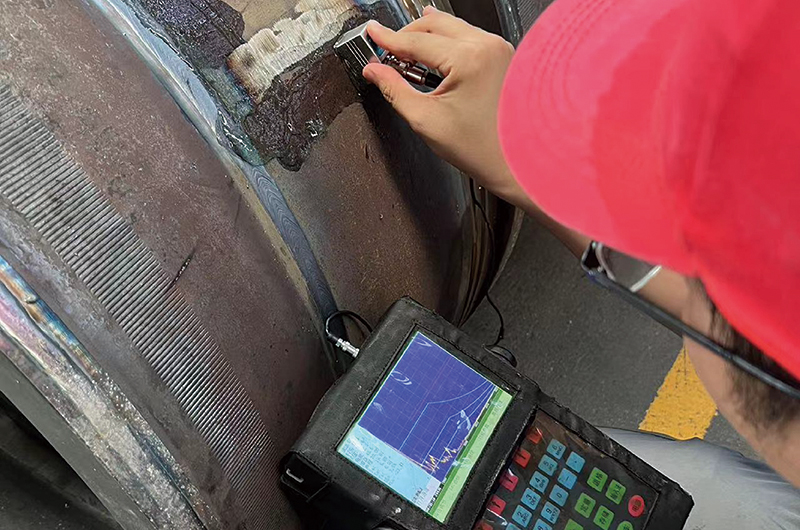

Non-destructive testing of product weld quality
Company Strength
Hongyuan Wheel Group(HYWG) was founded in 1996,it is professional manufacturer of rim for all kinds of off-the-road machinery and rim components,such as construction equipment, mining machinery, forklifts,industrial vehicles,agricultural machinery.
HYWG has advanced welding production technology for construction machinery wheels at home and abroad, an engineering wheel coating production line with the international advanced level, and an annual design and production capacity of 300,000 sets,and has a provincial-level wheel experiment center, equipped with various inspection and testing instruments and equipment, which provides a reliable guarantee for ensuring product quality.
Today it has more than 100 milion USD assets,1100 employees,4 manufacturing centers.Our business covers more than 20 countries and regions around the world, and the quality of all products has been recognized by Caterpillar, Volvo, Liebherr, Doosan, John Deere, Linde, BYD and other global oems.
HYWG will continue to develop and innovate, and continue to serve the customers wholeheartedly to create a brilliant future.
Why Choose Us
Our products include the wheels of all off-road vehicles and their upstream accessories, covering many fields, such as mining, construction machinery, agriculture industrial vehicles, forklifts, etc.
The quality of all products has been recognized by Caterpillar, Volvo, Liebherr, Doosan, John Deere, Linde, BYD and other global oems.
We have a R&D team composed of senior engineers and technical experts,focusing on the research and application of innovative technologies, and maintaining a leading position in the industry.
We have established a perfect after-sales service system to provide timely and efficient technical support and after-sales maintenance to ensure a smooth experience for customers during use.
Certificates

Volvo Certificates

John Deere Supplier Certificates

CAT 6-Sigma Certificates