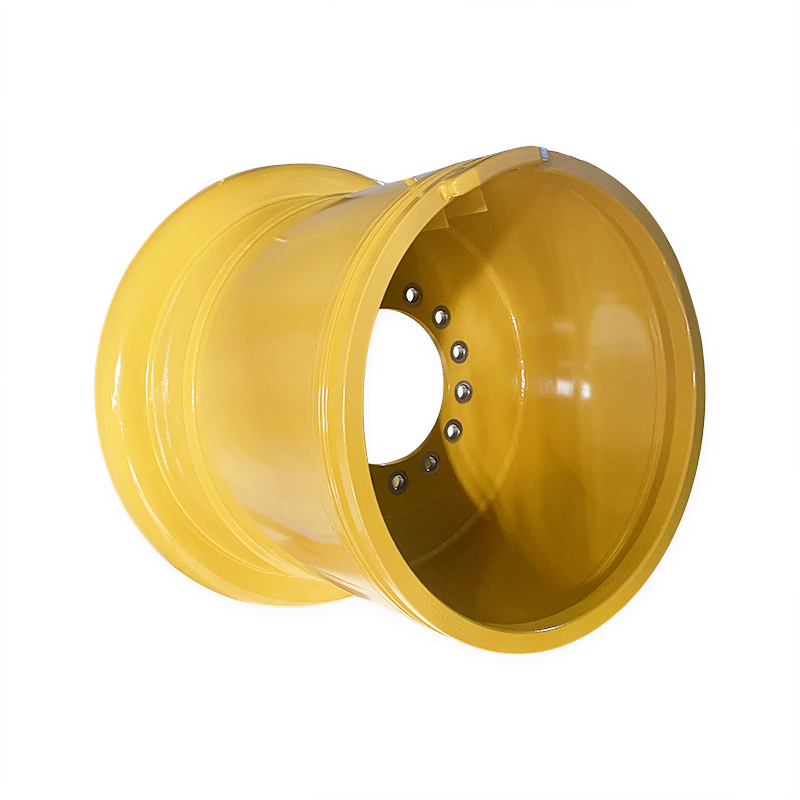
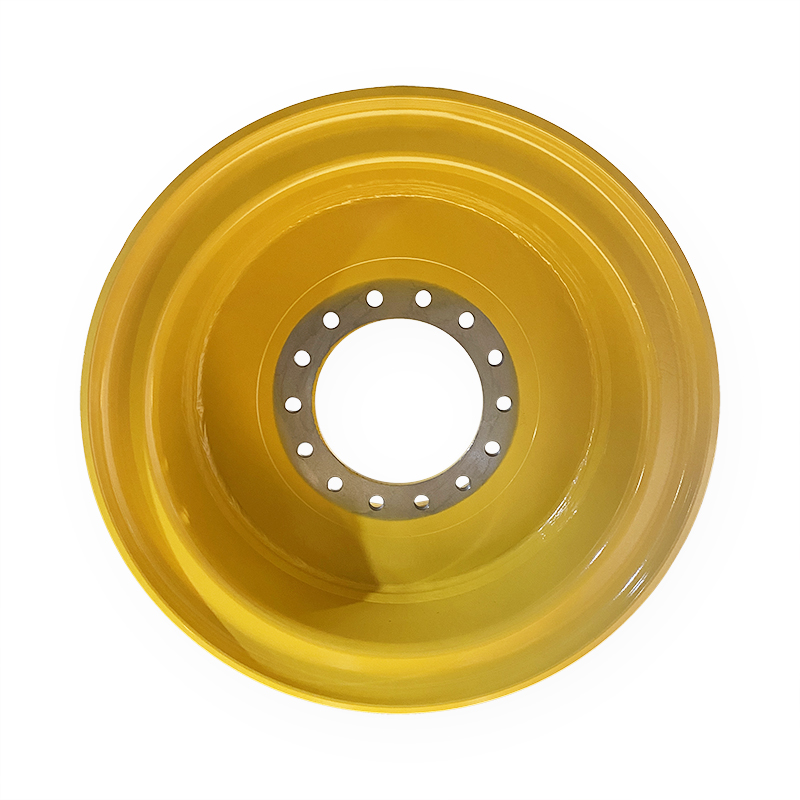
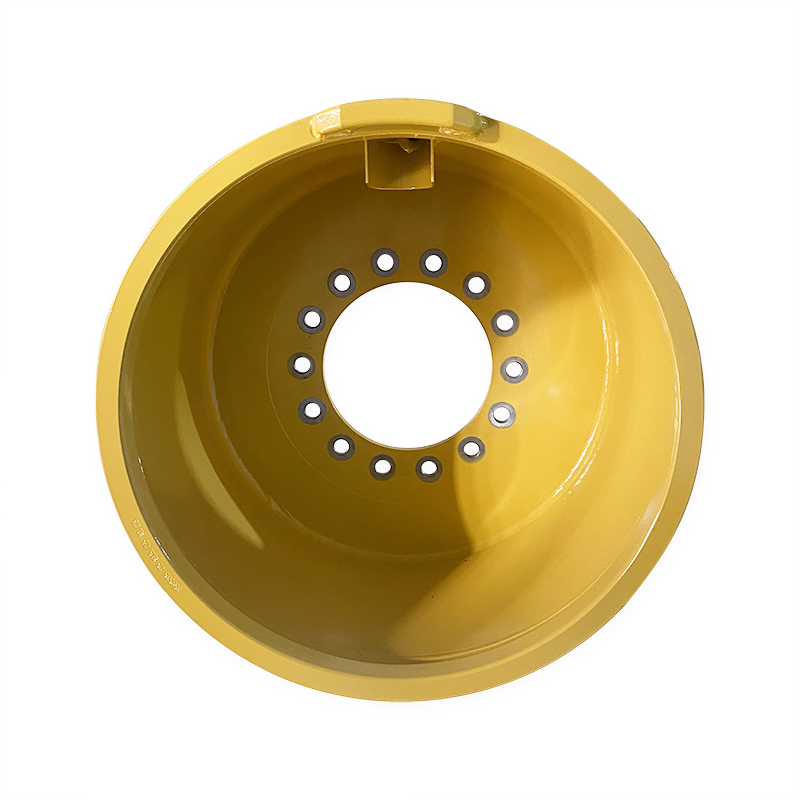
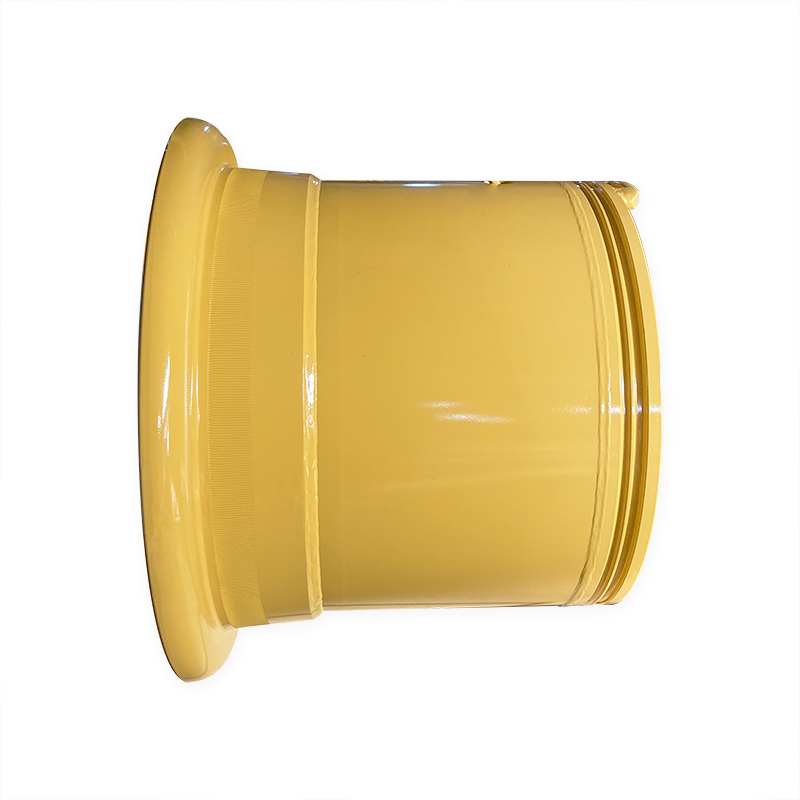
What is the manufacturing process for engineering vehicle wheel rims?
Construction vehicle wheel rims (such as those used for heavy vehicles such as excavators, loaders, mining trucks, etc.) are usually made of steel or aluminum alloy materials. The manufacturing process includes multiple steps, from raw material preparation, forming processing, welding assembly, heat treatment to surface treatment and final inspection. The following is a typical manufacturing process for construction vehicle wheel rims:
1. Raw material preparation
Material selection: Wheel rims are usually made of high-strength steel or aluminum alloy materials. These materials need to have good strength, durability, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance.
Cutting: Cutting raw materials (such as steel plates or aluminum alloy plates) into strips or sheets of specific sizes in preparation for subsequent processing.
2. Rim strip forming
Rolling: The cut metal sheet is rolled into a ring shape by a roll forming machine to form the basic shape of the rim strip. The force and angle need to be precisely controlled during the rolling process to ensure that the size and shape of the rim meet the design requirements.
Edge processing: Use special equipment to curl, reinforce or chamfer the edge of the rim to enhance the strength and rigidity of the rim.
3. Welding and assembly
Welding: The two ends of the formed rim strip are welded together to form a complete ring. This is usually done using automatic welding equipment (such as arc welding or laser welding) to ensure welding quality and consistency. After welding, grinding and cleaning are required to remove burrs and unevenness on the weld.
Assembly: Assemble the rim strip with other parts of the rim (such as the hub, flange, etc.), usually by mechanical pressing or welding. The hub is the part that is mounted to the tire, and the flange is the part that is connected to the vehicle's wheel axle.
4. Heat treatment
Annealing or quenching: The rims after welding or assembly are heat treated, such as annealing or quenching, to eliminate internal stress and improve the toughness and strength of the material. The heat treatment process needs to be carried out under precisely controlled temperature and time to ensure that the physical properties of the material meet the requirements.
5. Machining
Turning and drilling: CNC machine tools are used to perform precision machining on the rim, including turning the inner and outer surfaces of the rim, drilling holes (such as mounting bolt holes), and chamfering. These machining operations require high precision to ensure the balance and dimensional accuracy of the rim.
Balance calibration: Perform dynamic balance test on the processed rim to ensure its stability at high speed. Make necessary corrections and calibrations based on the test results.
6. Surface treatment
Cleaning and rust removal: Clean, rust and degrease the rims to remove the oxide layer, oil stains and other impurities on the surface.
Coating or plating: rims usually need to be treated with anti-corrosion treatment, such as spraying primer, topcoat or electroplating (such as electrogalvanizing, chrome plating, etc.). The surface coating not only provides a beautiful appearance, but also effectively prevents corrosion and oxidation, extending the service life of the rim.
7. Quality Inspection
Appearance inspection: Check the rim surface for defects such as scratches, cracks, bubbles or uneven coating.
Dimension inspection: Use special measuring tools to inspect the rim’s size, roundness, balance, hole position, etc. to ensure that it meets design specifications and quality standards.
Strength test: Static or dynamic strength test is performed on the rim, including compression, tension, bending and other properties, to ensure its reliability and durability in actual use.
8. Packaging and delivery
Packaging: Rims that pass all quality inspections will be packaged, usually in shock-proof and moisture-proof packaging to protect the rims from damage during transportation.
Shipping: The packaged rims will be shipped according to the order arrangement and transported to customers or dealers.
The manufacturing process of engineering car wheel rims involves multiple precision processing steps, including material preparation, molding, welding, heat treatment, machining and surface treatment, etc., to ensure that the rims have excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Each step requires strict quality control to ensure that the rims have long-term durability and reliability in harsh working environments.
We are the No.1 off-road wheel designer and manufacturer in China, and the world's leading expert in rim component design and manufacturing. All our products are designed and produced according to the highest quality standards, and we have more than 20 years of wheel manufacturing experience .
Our rims for construction vehicles and equipment cover a wide range of types, including wheel loaders, articulated trucks, graders, wheel excavators, and many other types . We are the original rim supplier in China for well-known brands such as Volvo, Caterpillar, Liebherr, and John Deere.
The 19.50-25/2.5 rims we provide for JCB wheel loaders have been highly recognized by customers. 19.50-25/2.5 is a 5PC structure rim for TL tires, commonly used for wheel loaders and ordinary vehicles.
The 19.50-25/2.5 rim is mainly used in heavy equipment such as construction machinery, mining vehicles, large loaders or rigid mining trucks.
Rims of this size have a stronger load-bearing capacity: wide rims combined with wide tires can effectively disperse pressure, improve the load capacity and stability of the entire vehicle, and are particularly suitable for heavy-load conditions.
It is suitable for large-size tires , especially heavy-duty tires such as 23.5R25 and 26.5R25. It increases the contact area between the tire and the ground, reduces the pressure per unit area, and is conducive to the passability on soft ground and slippery conditions. At the same time, wider rims and tires can effectively improve the vehicle's anti-roll ability when turning. It is used in large loaders, rigid mining vehicles, scrapers and other equipment.
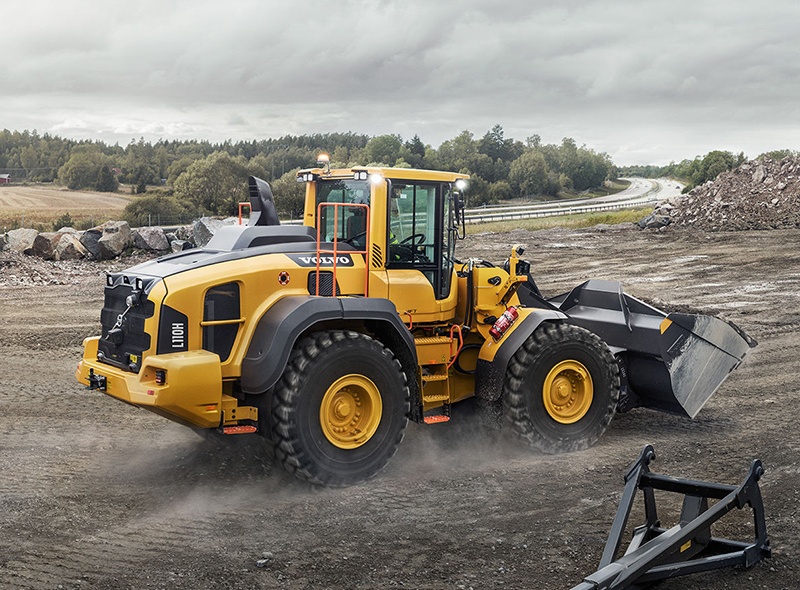
How to use a wheel loader correctly?
Wheel loaders are a common type of construction machinery, mainly used in earthwork, mining, construction and other occasions to load, transport, stack and clean materials. Proper use of wheel loaders can not only improve work efficiency, but also ensure operational safety. The following are the basic methods and steps for using wheel loaders:
1. Preparation before operation
Check the equipment: Check the appearance of the wheel loader and whether all its components are in good condition, including tires (check tire pressure and wear), hydraulic system (whether the oil level is normal and whether there is any leakage), engine (check engine oil, coolant, fuel, air filter, etc.).
Safety check: Make sure all safety devices are functioning properly, such as brakes, steering systems, lights, horns, warning signs, etc. Check whether the seat belts, safety switches and fire extinguishers in the cab are in good condition.
Environmental inspection: Check whether there are any obstacles or potential hazards at the work site, and ensure that the ground is solid and flat, without obvious obstacles or other potential hazards.
Start the equipment: Get in the cab and fasten your seat belt. Start the engine according to the instructions in the operator's manual, wait for the equipment to warm up (especially in cold weather), and observe the indicator lights and alarm systems on the dashboard to ensure that all systems are normal.
2. Basic operation of wheel loader
Adjust your seat and mirrors: Adjust your seat to a comfortable position and make sure you can operate the control levers and pedals easily. Adjust your rearview and side mirrors to ensure a clear view.
Control lever:
Bucket operating lever: used to control the lifting and tilting of the bucket. Pull the lever backward to raise the bucket, push it forward to lower it; push it left or right to control the tilt of the bucket.
Travel control lever: Usually located on the right hand side of the driver, used for forward and reverse. After selecting forward or reverse gear, gradually depress the accelerator pedal to control the speed.
Driving operation:
Starting: Select the appropriate gear (usually 1st or 2nd), slowly press the accelerator pedal, start gently, and avoid sudden acceleration.
Steering: Turn the steering wheel slowly to control the steering, avoid sharp turns at high speeds to prevent rollover. Maintain a steady speed to ensure the vehicle is stable.
Loading operation:
Approach the material pile: Approach the material pile at a low speed, make sure the bucket is stable and close to the ground, and prepare to shovel in the material.
Shovel material: When the bucket contacts the material, gradually lift the bucket and tilt it backwards to shovel the right amount of material. Make sure the bucket is evenly loaded to avoid eccentric loading.
Lift the bucket: After loading is complete, lift the bucket to the proper transport height, avoiding being too high or too low to maintain a clear view and stability.
Moving and unloading: transport the material to the designated location at a low speed, then slowly lower the bucket and unload the material smoothly. When unloading, make sure the bucket is balanced and do not dump it suddenly.
3. Key points for safe operation
Maintain stability: Avoid sideways driving or sharp turns on slopes to maintain the stability of the loader. When driving on a slope, try to go straight up and down to avoid the risk of rollover.
Avoid overloading: Load the loader reasonably according to its load capacity and avoid overloading. Overloading will affect operational safety, increase equipment wear and shorten equipment life.
Maintain a clear field of vision: During loading and transport, ensure that the driver has a good field of vision, especially when operating in complex conditions or crowded areas.
Operate slowly: When loading and unloading, always operate at a low speed and avoid sudden acceleration or braking. Especially when driving the machine close to the material pile, operate it gently.
4. Maintenance and care after operation
Clean the equipment: After work, clean the wheel loader, especially areas such as the bucket, engine air intake and radiator where dust and dirt tend to accumulate.
Check for wear: Check tires, buckets, hinge points, hydraulic lines, cylinders and other parts for damage, looseness or oil leakage.
Filling fuel and lubrication: Fill the loader with fuel as needed, check and replenish hydraulic oil, engine oil and other lubricants. Keep all lubrication points well lubricated.
Record equipment status: Keep operation records and equipment status records, including operating hours, maintenance status, fault records, etc., to facilitate daily management and maintenance.
5. Emergency handling
Brake failure: Immediately shift to a lower gear, use the engine to slow down, and slowly come to a stop; if necessary, apply the emergency brake.
Hydraulic system failure: If the hydraulic system fails or leaks, stop operation immediately, park the loader in a safe place, and inspect or repair it.
Equipment failure alarm: If a warning signal appears on the instrument panel, immediately check the cause of the failure and decide whether to continue the operation or perform repairs based on the situation.
The use of wheel loaders requires strict compliance with operating procedures, familiarity with various control devices and functions, good driving habits, regular maintenance and care, and always paying attention to operational safety. Reasonable use and maintenance can not only extend the life of the equipment, but also improve operating efficiency and ensure the safety of the construction site.
We not only produce engineering machinery rims , but also have a wide range of products including mining vehicle rims, forklift rims, industrial rims, agricultural rims and other rim accessories and tires .
The following are the various sizes of rims that our company can produce in different fields:
Engineering machinery size:
| 8.00-20 | 7.50-20 | 8.50-20 | 10.00-20 | 14.00-20 | 10.00-24 | 10.00-25 |
| 11.25-25 | 12.00-25 | 13.00-25 | 14.00-25 | 17.00-25 | 19.50-25 | 22.00-25 |
| 24.00-25 | 25.00-25 | 36.00-25 | 24.00-29 | 25.00-29 | 27.00-29 | 13.00-33 |
Mine rim size:
| 22.00-25 | 24.00-25 | 25.00-25 | 36.00-25 | 24.00-29 | 25.00-29 | 27.00-29 |
| 28.00-33 | 16.00-34 | 15.00-35 | 17.00-35 | 19.50-49 | 24.00-51 | 40.00-51 |
| 29.00-57 | 32.00-57 | 41.00-63 | 44.00-63 |
Forklift wheel rim size:
| 3.00-8 | 4.33-8 | 4.00-9 | 6.00-9 | 5.00-10 | 6.50-10 | 5.00-12 |
| 8.00-12 | 4.50-15 | 5.50-15 | 6.50-15 | 7.00-15 | 8.00-15 | 9.75-15 |
| 11.00-15 | 11.25-25 | 13.00-25 | 13.00-33 |
Industrial vehicle rim dimensions:
| 7.00-20 | 7.50-20 | 8.50-20 | 10.00-20 | 14.00-20 | 10.00-24 | 7.00x12 |
| 7.00x15 | 14x25 | 8.25x16.5 | 9.75x16.5 | 16x17 | 13x15.5 | 9x15.3 |
| 9x18 | 11x18 | 13x24 | 14x24 | DW14x24 | DW15x24 | 16x26 |
| DW25x26 | W14x28 | 15x28 | DW25x28 |
Agricultural machinery wheel rim size:
| 5.00x16 | 5.5x16 | 6.00-16 | 9x15.3 | 8LBx15 | 10LBx15 | 13x15.5 |
| 8.25x16.5 | 9.75x16.5 | 9x18 | 11x18 | W8x18 | W9x18 | 5.50x20 |
| W7x20 | W11x20 | W10x24 | W12x24 | 15x24 | 18x24 | DW18Lx24 |
| DW16x26 | DW20x26 | W10x28 | 14x28 | DW15x28 | DW25x28 | W14x30 |
| DW16x34 | W10x38 | DW16x38 | W8x42 | DD18Lx42 | DW23Bx42 | W8x44 |
| W13x46 | 10x48 | W12x48 | 15x10 | 16x5.5 | 16x6.0 |
Our products are of world-class quality.

Post time: Sep-14-2024